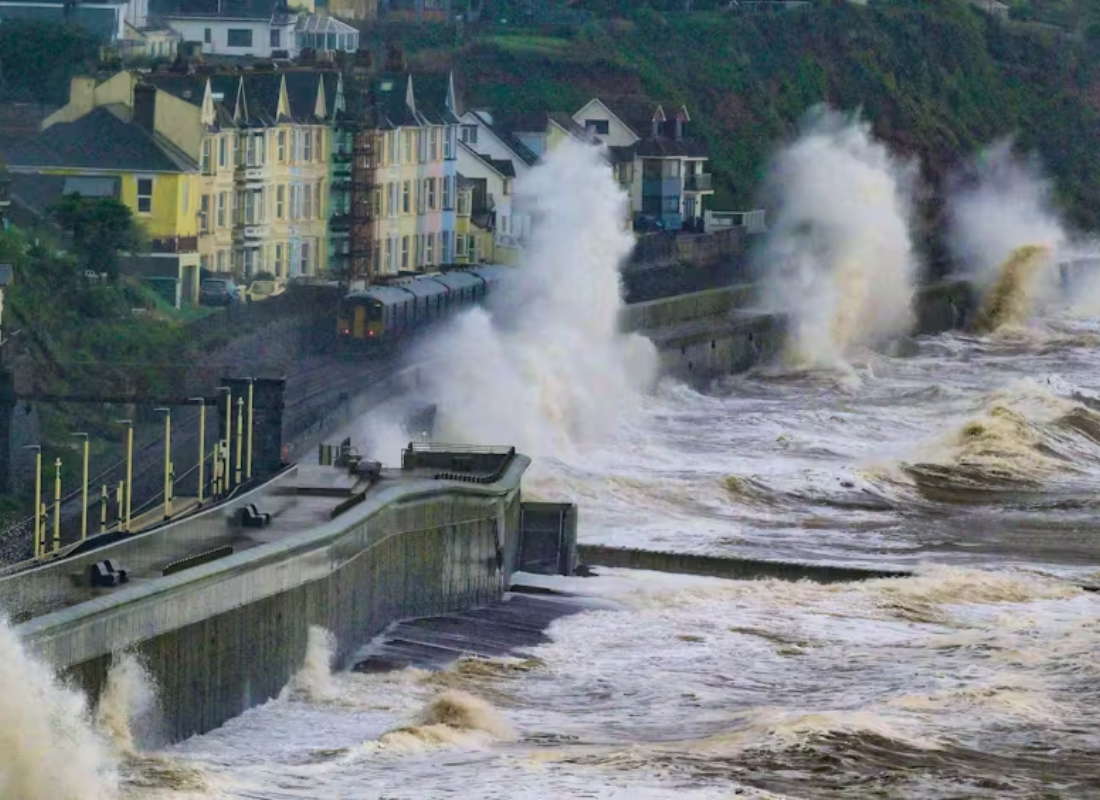
Sea level rise poses a significant and escalating threat to coastal communities worldwide. Understanding its causes, impacts, and the necessary adaptive measures is crucial for mitigating its effects.
Understanding Sea Level Rise
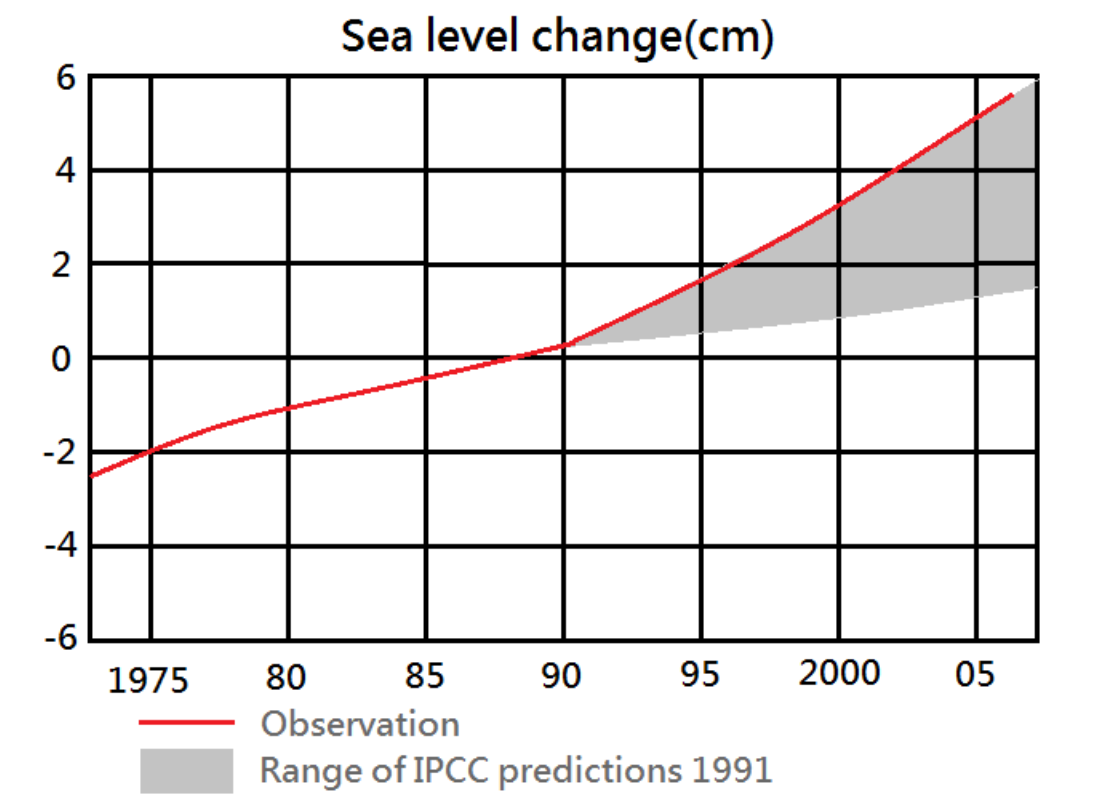
Global average sea levels have risen 8–9 inches (21–24 centimeters) since 1880, with the rate of increase accelerating in recent decades.
 Impacts on Coastal Communities
Impacts on Coastal Communities
The consequences of rising sea levels are profound, particularly for the approximately 40% of the U.S. population residing in coastal areas.
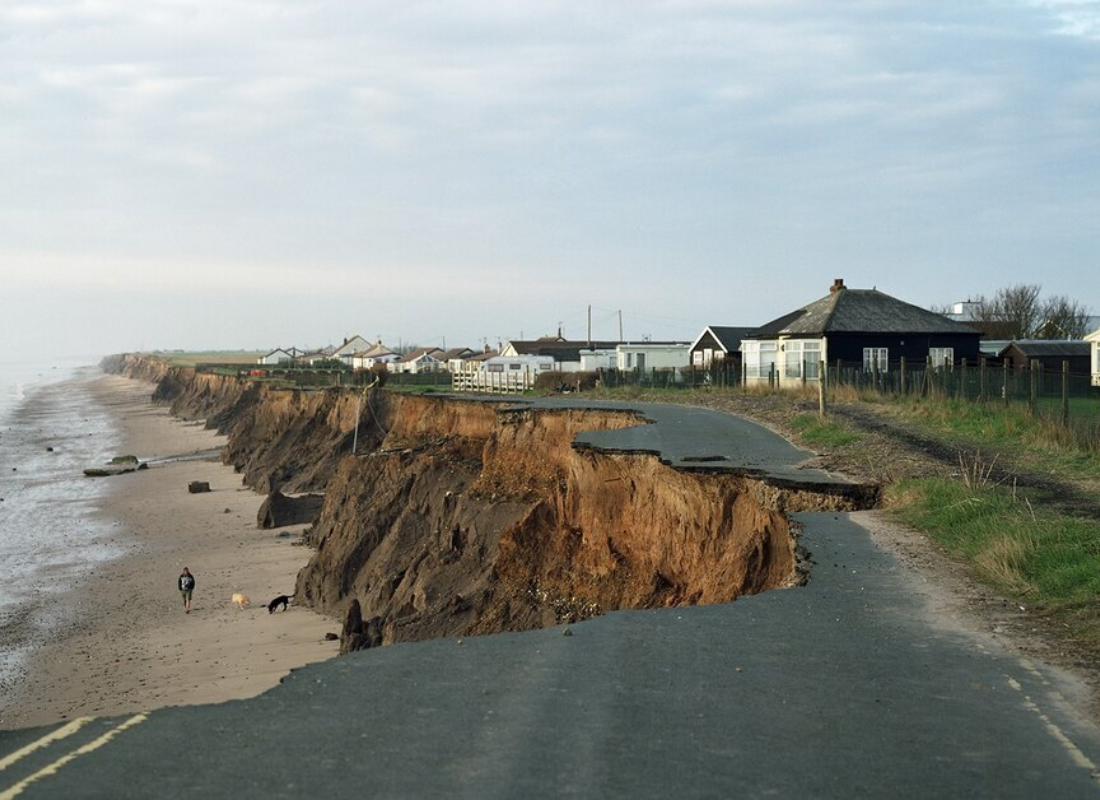 Increased Flooding
Increased Flooding
Higher sea levels lead to more frequent and severe flooding. High tide flooding, often referred to as “nuisance flooding,” has become more common, disrupting daily life and causing economic losses.
- Erosion and Habitat Loss
Coastal erosion accelerates as sea levels rise, leading to the loss of beaches and wetlands. This erosion threatens property, infrastructure, and vital ecosystems that serve as natural barriers against storms.
- Saltwater Intrusion
Rising seas can cause saltwater to infiltrate freshwater aquifers, contaminating drinking water supplies and harming agricultural lands. 
4. Displacement of Populations
As coastal areas become uninhabitable, populations may be forced to relocate. In the U.S., up to 13 million people could face displacement due to permanent flooding by 2100.
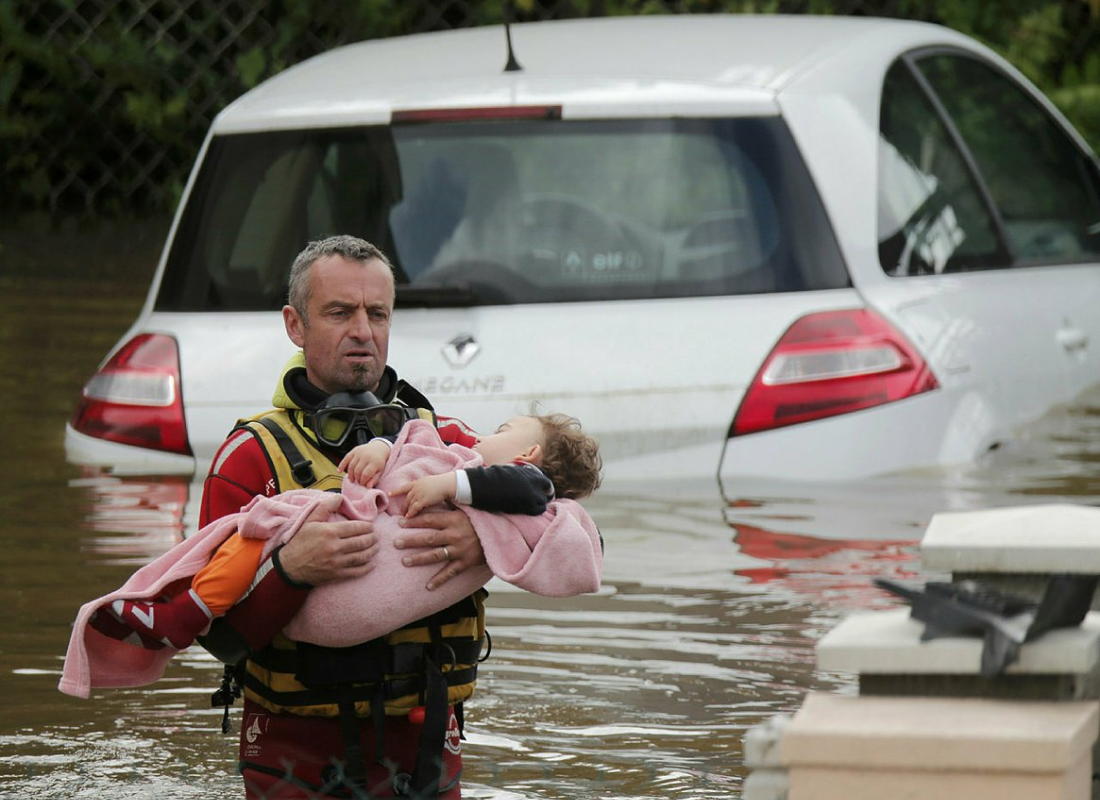

Case Studies
- Gwadar, Pakistan
The coastal city of Gwadar has experienced intensified rainfall and coastal erosion, leading to frequent flooding and infrastructure damage. These changes threaten the livelihoods of local communities, particularly those reliant on fishing.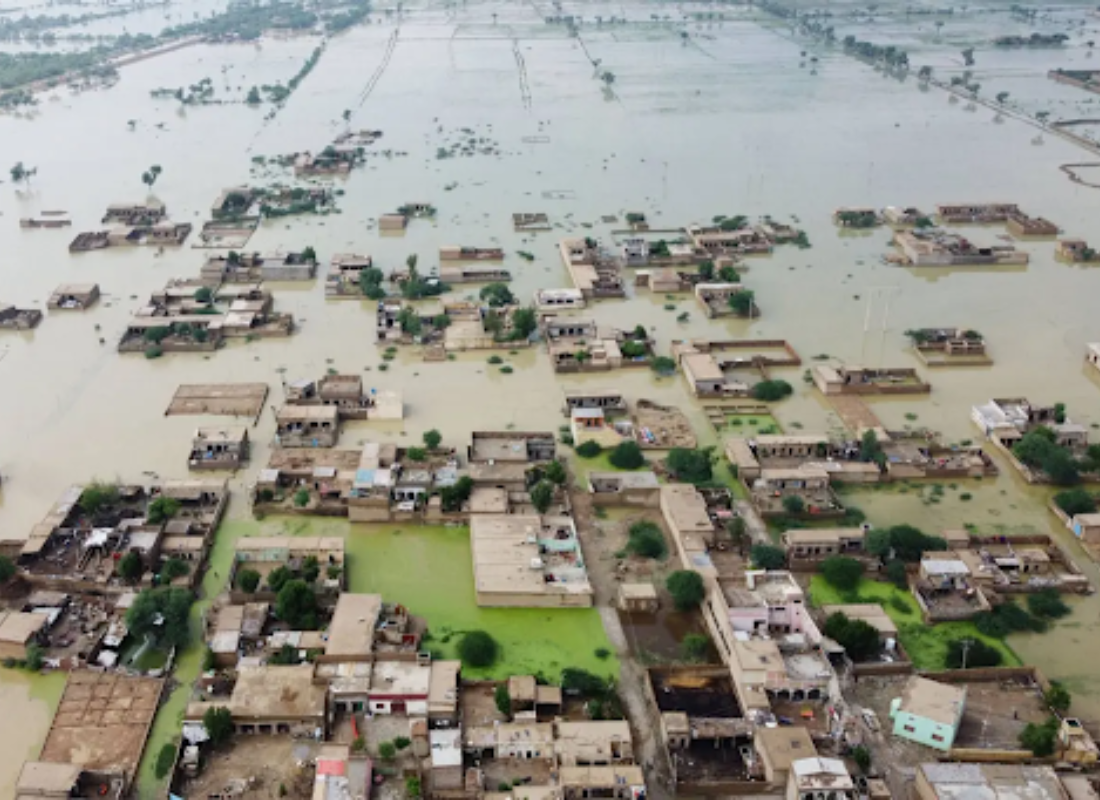 
- Shinnecock Nation, New York
The Shinnecock Nation faces significant land loss due to rising sea levels and coastal erosion. Projections indicate that nearly half of their land may flood by 2050, prompting considerations of relocation and other adaptive measures.
Global Projections
By 2050, approximately 800 million people will reside in cities where sea levels could rise by more than half a meter, increasing the risk of coastal flooding and storm surges. 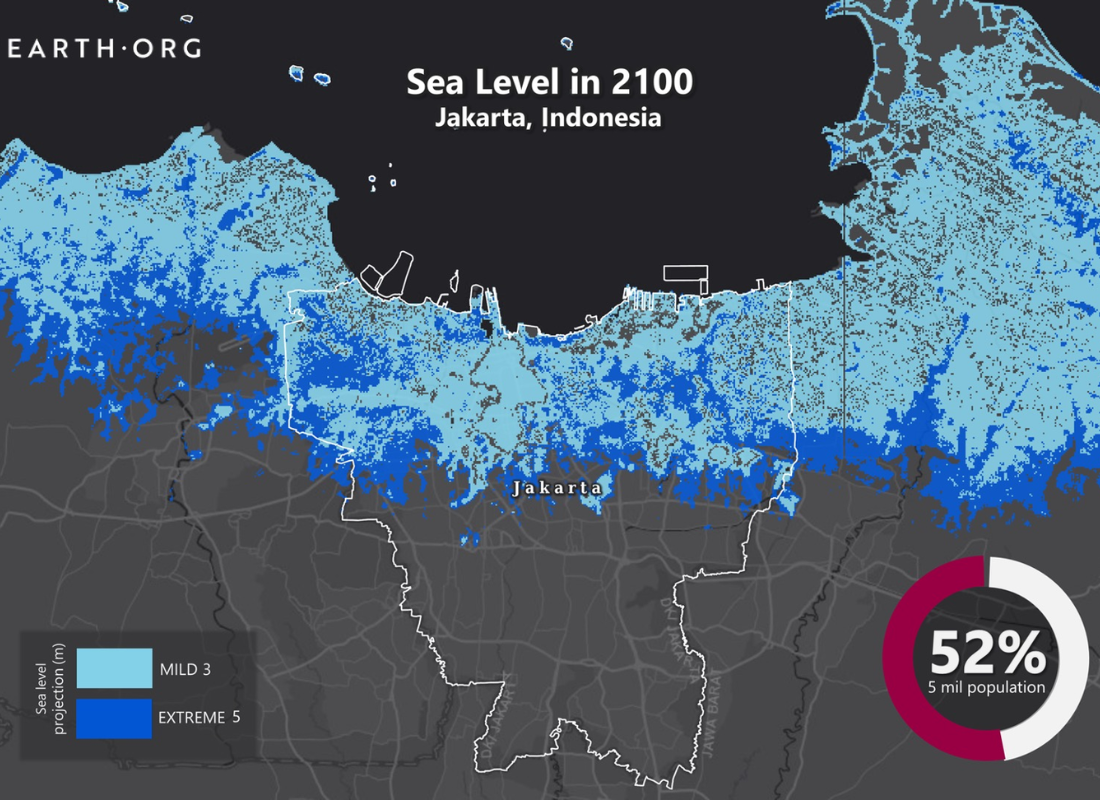
Adaptive Measures
- Infrastructure Enhancements
Constructing sea walls, levees, and floodgates can provide physical barriers against rising waters. However, these solutions require significant investment and ongoing maintenance.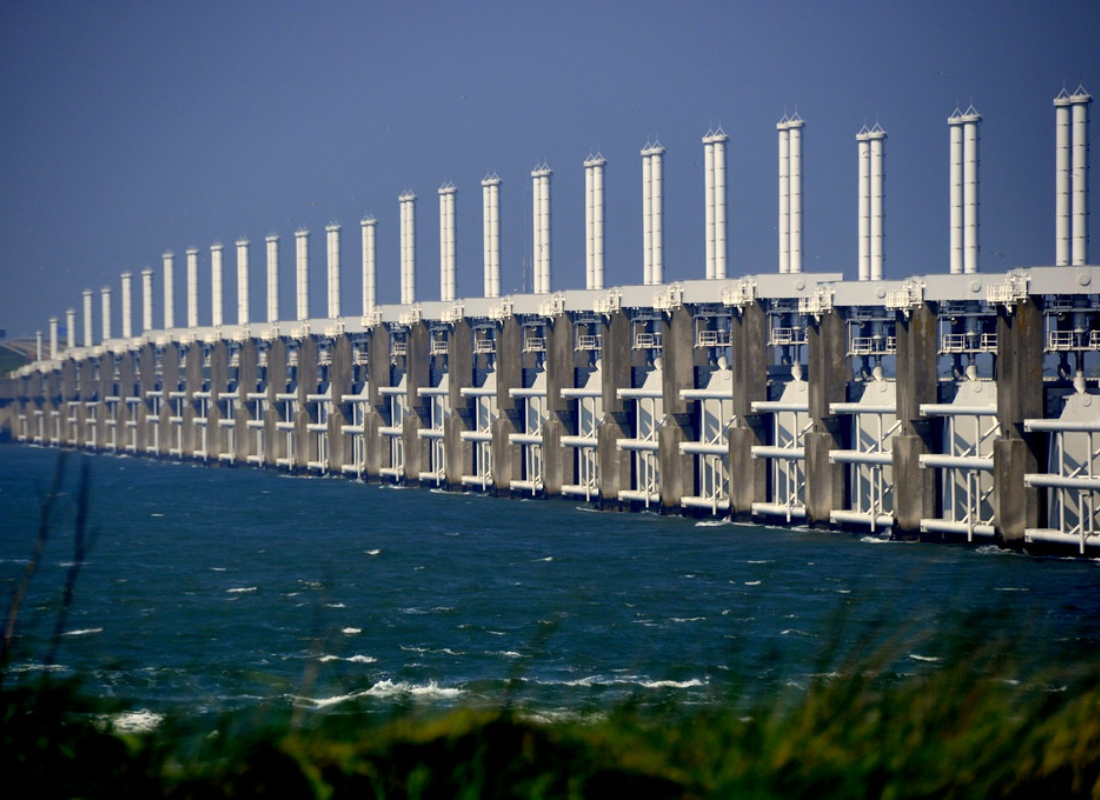
- Managed Retreat
In some cases, relocating communities away from vulnerable coastal areas may be the most viable long-term solution. This strategy necessitates careful planning to address social, economic, and cultural implications.
- Ecosystem Restoration
Restoring mangroves, wetlands, and coral reefs can enhance natural defenses against sea-level rise while preserving biodiversity.
Conclusion
Rising sea levels present an urgent challenge to coastal communities globally. Proactive adaptation strategies, informed by scientific research and community engagement, are essential to mitigate the adverse effects and safeguard the livelihoods of those residing in these vulnerable areas.




