
Water, the essence of life, has become a scarce resource, and the world is facing a crisis of unprecedented proportions – water scarcity.
This global challenge transcends geographical boundaries, affecting both developed and developing nations alike.
The repercussions of depleting water resources are far-reaching, impacting ecosystems, agriculture, human health, and the overall sustainability of our planet.
This article explores the causes, consequences, and potential solutions to address the alarming issue of water scarcity.
Causes of Water Scarcity:
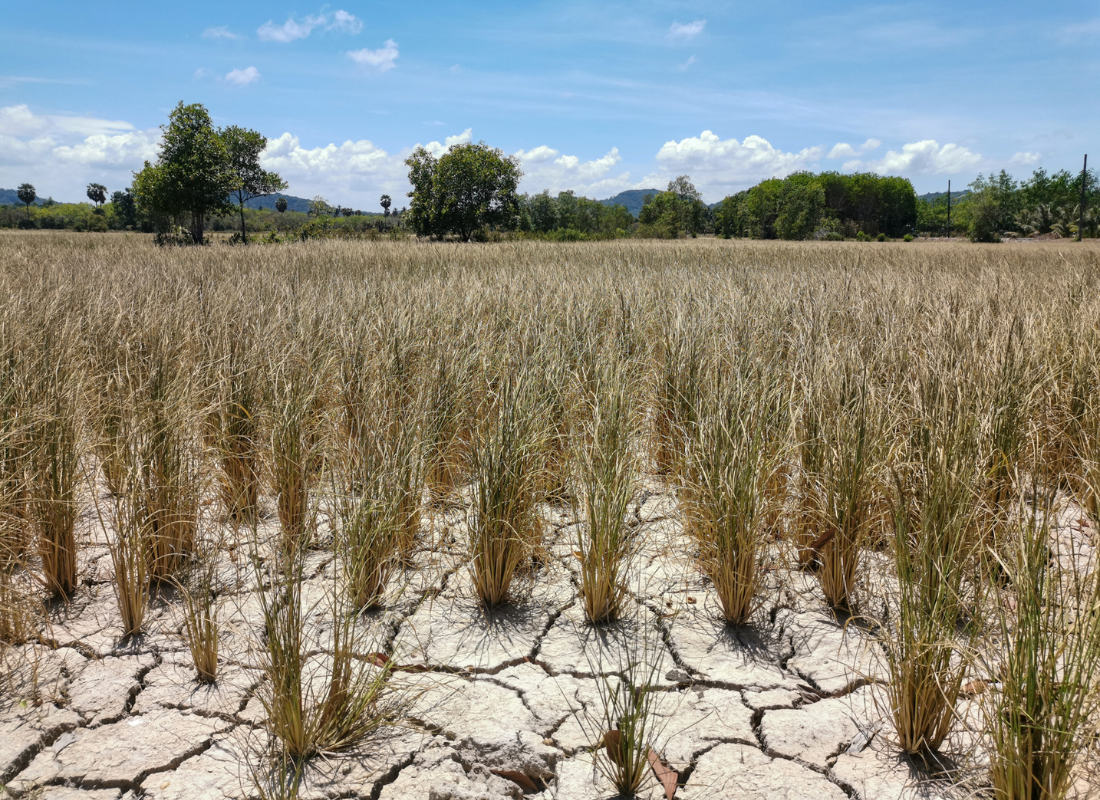

- Population Growth: One of the primary drivers of water scarcity is the exponential growth of the global population. As more people inhabit the planet, the demand for water increases for domestic use, agriculture, and industrial activities. Unfortunately, water resources are finite, and the current rate of population growth is outpacing our ability to provide sustainable water solutions.
- Climate Change: Climate change exacerbates water scarcity through altered precipitation patterns, increased temperatures, and extreme weather events. Regions that once relied on predictable rainfall are experiencing droughts, while others face intensified floods. These climate-induced changes disrupt the natural water cycle, making water resources less reliable and leading to increased water stress.
- Unsustainable Agricultural Practices: Agriculture is a major consumer of water, and unsustainable farming practices further strain water resources. Excessive irrigation, inefficient water use, and the cultivation of water-intensive crops contribute to the depletion of aquifers and rivers. Adopting water-efficient agricultural techniques and promoting sustainable farming practices are essential steps in mitigating water scarcity.
- Urbanization: Rapid urbanization is another significant factor contributing to water scarcity. As more people move to cities, the demand for water in urban areas rises sharply. Cities often rely on distant water sources, leading to long transport routes and increased energy consumption. Moreover, the expansion of impervious surfaces in urban areas reduces natural water infiltration, exacerbating runoff and diminishing groundwater recharge.
Consequences of Water Scarcity:
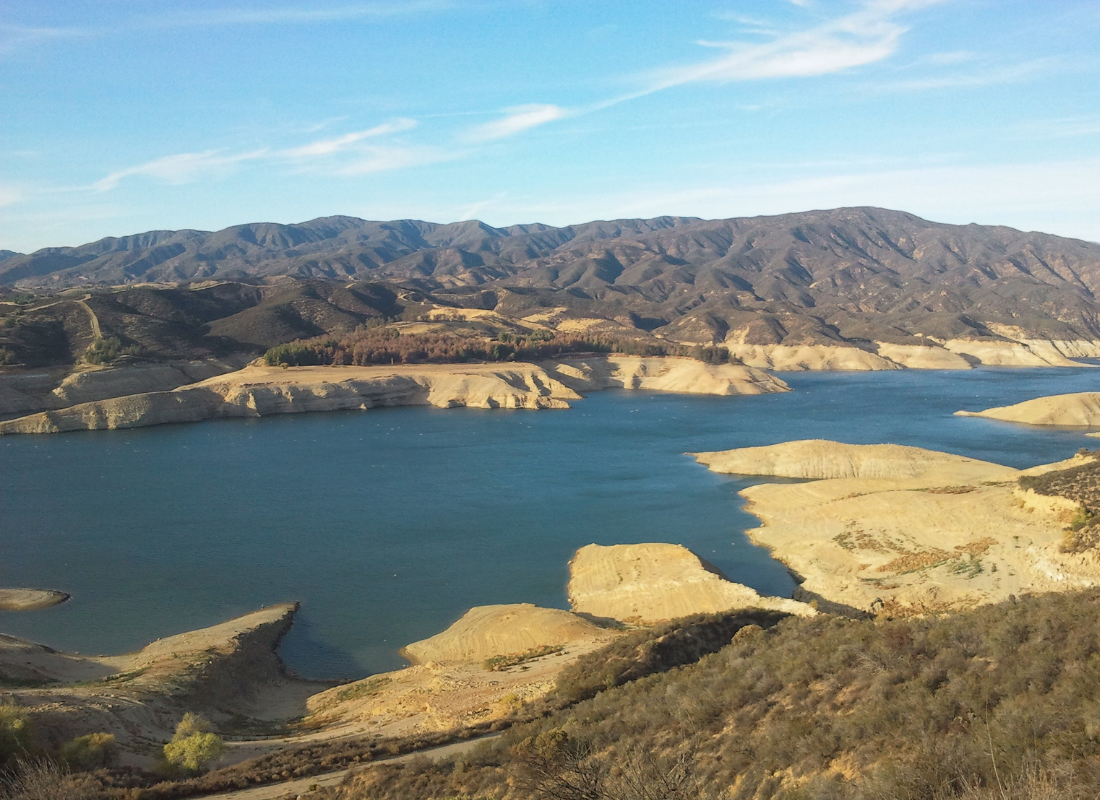

- Ecological Impact: Depleted water resources have severe consequences for ecosystems. Aquatic habitats are disrupted, leading to the decline of freshwater species. Wetlands, crucial for biodiversity and water purification, suffer from reduced water levels, affecting migratory patterns and breeding grounds for various species.
- Agricultural Challenges: Agriculture, a cornerstone of human survival, faces significant challenges due to water scarcity. Crop yields decline, food prices rise, and farmers struggle to maintain their livelihoods. Smallholder farmers in developing nations are particularly vulnerable, as they often lack the resources to implement water-efficient technologies.
- Health and Sanitation: Water scarcity has direct implications for human health. Limited access to clean water leads to waterborne diseases, such as cholera and dysentery. Poor sanitation and hygiene exacerbate the problem, creating a cycle of illness that disproportionately affects vulnerable populations in impoverished regions.
- Socioeconomic Impacts: Water scarcity is not only an environmental concern but also a socioeconomic challenge. Competing demands for water resources can lead to conflicts among communities, regions, and even nations. Disparities in access to water exacerbate existing social inequalities, with marginalized populations often bearing the brunt of the crisis.
Potential Solutions:

- Water Conservation and Efficiency: Promoting water conservation and efficiency is crucial in addressing water scarcity. Individuals, industries, and agriculture must adopt practices that reduce water waste. Implementing water-saving technologies, fixing leaks, and optimizing irrigation systems are effective measures to ensure more efficient water use.
- Sustainable Agriculture: Adopting sustainable agricultural practices is essential for preserving water resources. Techniques such as precision farming, rainwater harvesting, and agroforestry can improve water efficiency in agriculture. Additionally, promoting the cultivation of drought-resistant crops helps mitigate the impact of water scarcity on food production.
- Integrated Water Management: Effective water management involves considering the entire water cycle and integrating policies across various sectors. This includes watershed management, protection of natural water sources, and the development of comprehensive water-use plans that prioritize conservation and sustainability.
- Investment in Water Infrastructure: Investment in water infrastructure is crucial for enhancing water security. This includes the construction and maintenance of dams, reservoirs, and water treatment facilities. Developing efficient water storage systems helps manage water availability during periods of scarcity and abundance.
- Climate Change Mitigation and Adaptation: Addressing the root causes of water scarcity requires a concerted effort to mitigate climate change and adapt to its impacts. Reducing greenhouse gas emissions, transitioning to renewable energy sources, and implementing climate-resilient infrastructure are integral components of a comprehensive strategy.
Conclusion:
Water scarcity is a complex and multifaceted challenge that demands urgent attention and global cooperation.
The consequences of depleting water resources are evident across ecosystems, agriculture, and human health, affecting both developed and developing nations.
Sustainable solutions must be implemented at individual, community, and governmental levels to navigate this global crisis effectively.
By adopting water-efficient practices, promoting sustainable agriculture, investing in water infrastructure, and addressing the root causes of climate change, we can work towards ensuring a secure and sustainable water future.
Only through collaborative efforts and a shared commitment to responsible water management can we hope to overcome the looming threat of water scarcity and ensure that future generations inherit a planet with abundant and accessible water resources.




