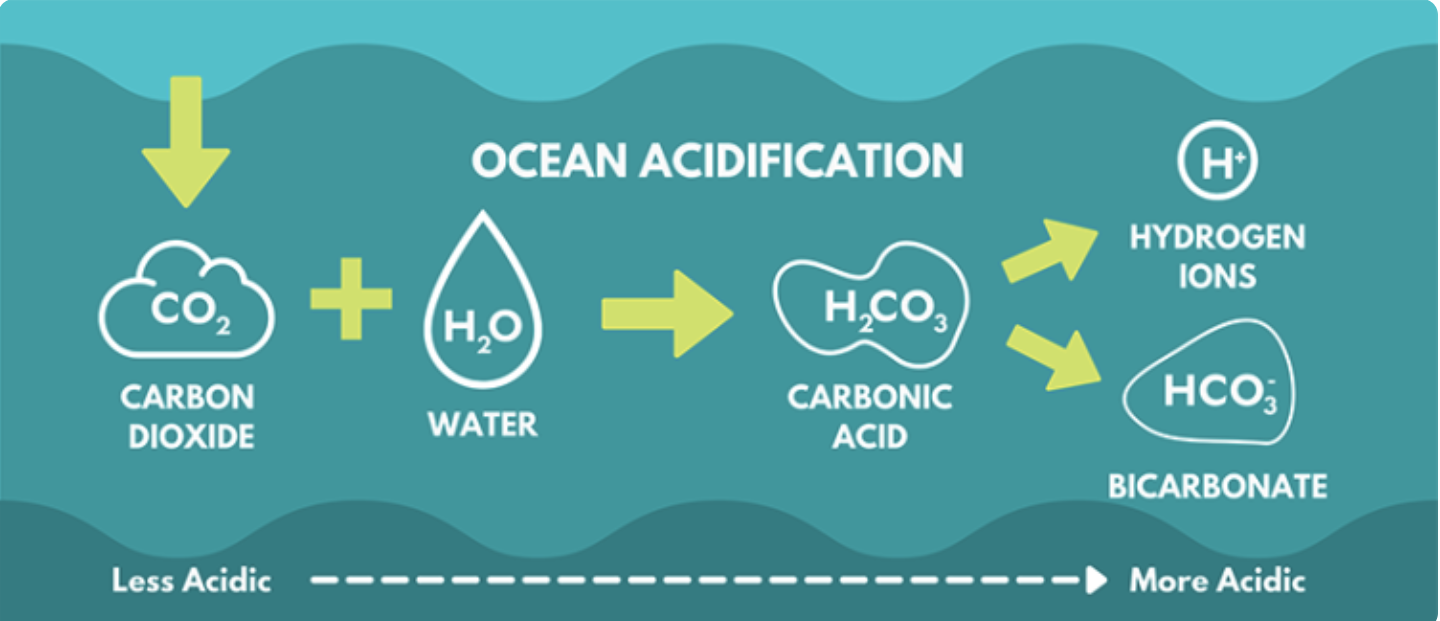
The continuous lowering of the pH levels of Earth’s oceans, which is principally brought on by the absorption of carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere, is referred to as ocean acidification.
When CO2 dissolves in seawater, it produces carbonic acid, which lowers the pH of the ocean and increases its acidity, and the lower the pH values, the greater the acidity.
The increased CO2 emissions brought on by human activities like the burning of fossil fuels and deforestation are the main contributors to ocean acidification. About one-third of the carbon dioxide released into the atmosphere is naturally absorbed by the ocean, triggering chemical processes that change the chemistry of the salt water.

Marine habitats suffer from a number of negative effects of ocean acidification. One of the major effects is the decrease in carbonate ions’ availability, which is essential for creatures that build shells, such as corals, mollusks, and some planktonic species.

Habitat loss as a result of ocean acidification.
Ocean acidification’s effects can be felt throughout the entire marine food chain. Shell development and growth are challenging for corals and shellfish like oysters and clams.
Other species that depend on them for food or habitat may also be affected by these effects. Ultimately, it may throw off the equilibrium of marine ecosystems and have a domino effect on fish populations, marine biodiversity, and the ocean’s overall health.

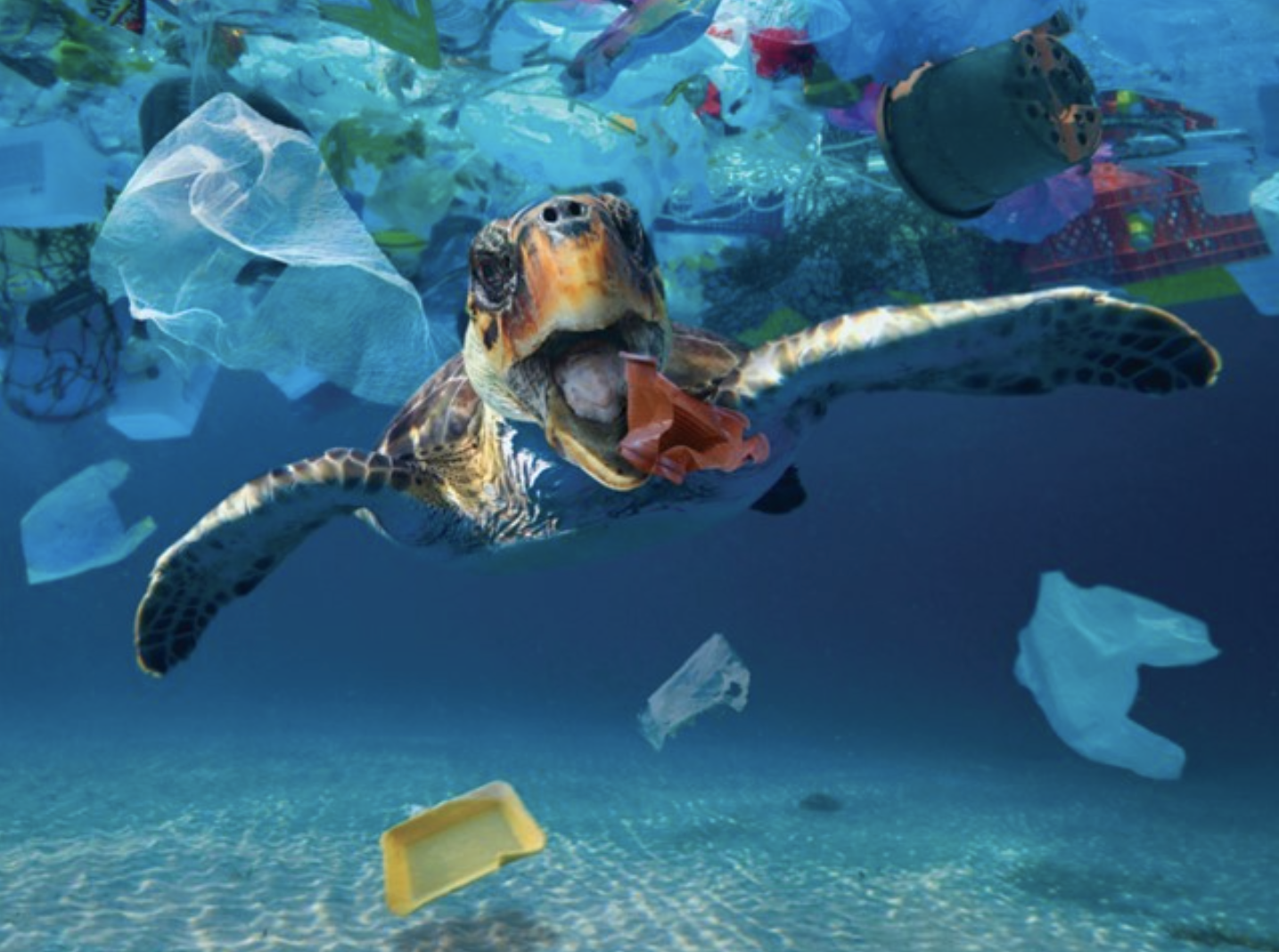
Sea turtles may be indirectly impacted by ocean acidification due to its effects on their habitats and food supplies. Sea turtles may be impacted by ocean acidification in the following ways:
Coral reef degradation:
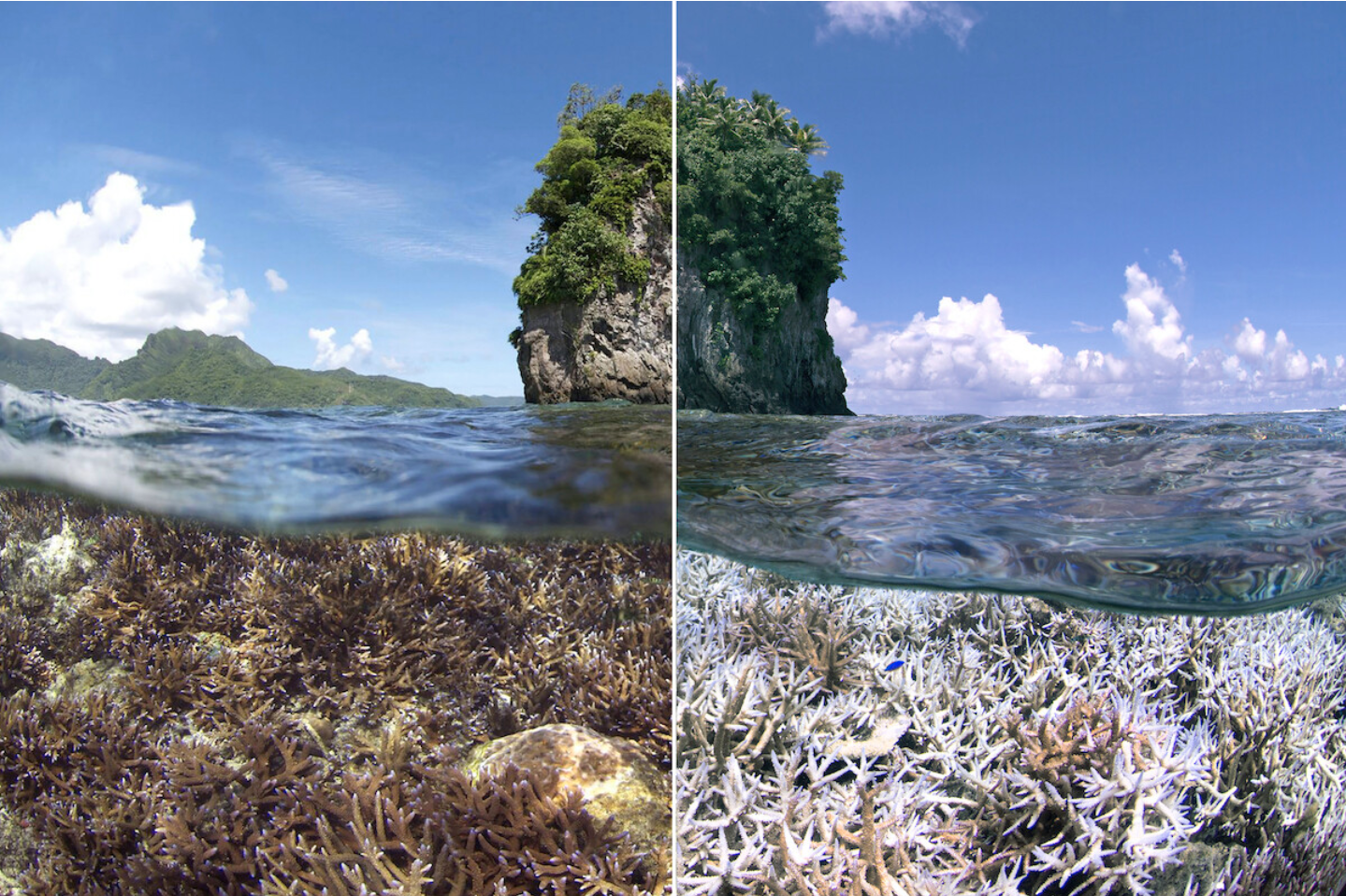
Ocean acidification can cause coral reefs, which are crucial sea turtle homes, to deteriorate. Diverse marine creatures, including young sea turtles, can find food and shelter under corals.
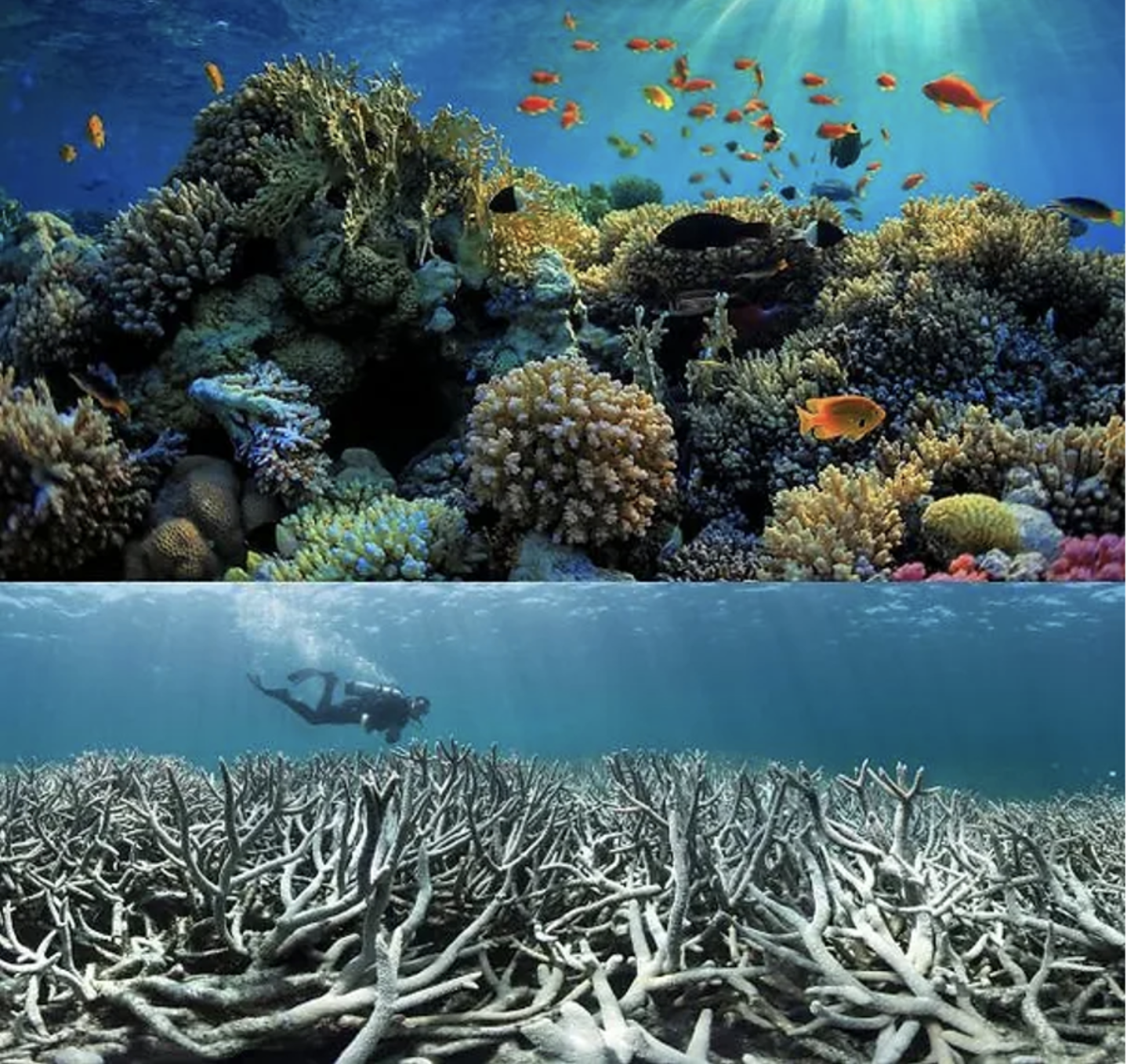

Ocean acidification can make it harder for sea turtles to find adequate habitats because it impacts the growth and health of corals.
Modified food availability:
The abundance and accessibility of some food sources for sea turtles may change as a result of ocean acidification. For instance, seagrass meadows serve as the main source of food for several species of sea turtles, such as green sea turtles.

Ocean acidification may have a deleterious effect on seagrasses, thereby diminishing their abundance and nutritional value. Sea turtle growth and reproductive success may be hampered if seagrass meadows become less abundant.
Therefore, reducing the quantity of CO2 released into the atmosphere is necessary to address ocean acidification.
This can be accomplished by consuming fewer fossil fuels, switching to renewable energy sources, and putting legislation in place to support sustainable activities.
It’s crucial to remember that while ocean acidification causes serious problems for sea turtles, it’s not the only danger they must contend with. Along with habitat loss, pollution, climate change, entanglement in fishing gear, and poaching, sea turtles also face additional urgent problems.
It is essential for the long-term survival and well-being of sea life to address these more general conservation challenges and implement sustainable methods.




