
As we enter 2025, the push for sustainable food systems has never been more urgent. Food production is one of the largest contributors to greenhouse gas emissions, deforestation, and water consumption. With the world facing environmental crises, from soil degradation to biodiversity loss, innovation in food sustainability is critical.
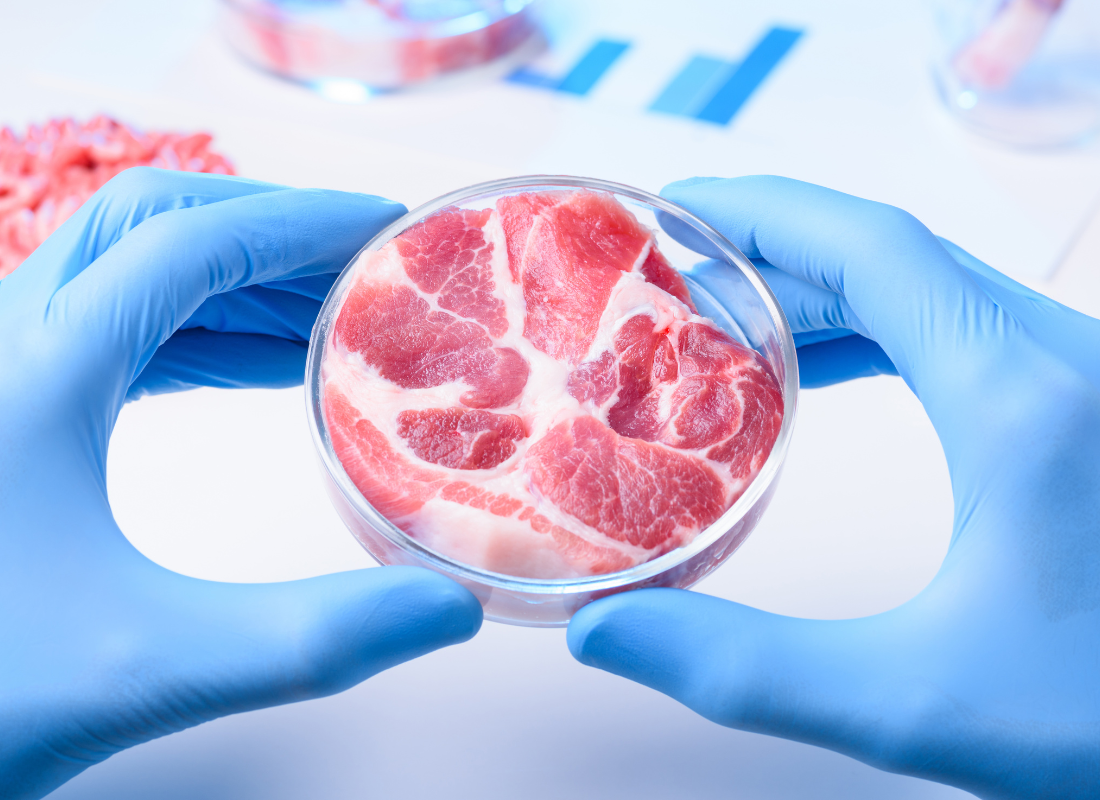 In 2025, several food trends are poised to reshape the industry, offering hope for a more eco-friendly future. These trends—including regenerative farming, plant-based alternatives, lab-grown meat, and more—are transforming how food is produced, consumed, and valued. In this article, we’ll explore each of these sustainable food trends and highlight how companies can contribute to a healthier planet.
In 2025, several food trends are poised to reshape the industry, offering hope for a more eco-friendly future. These trends—including regenerative farming, plant-based alternatives, lab-grown meat, and more—are transforming how food is produced, consumed, and valued. In this article, we’ll explore each of these sustainable food trends and highlight how companies can contribute to a healthier planet.
Regenerative Agriculture: Restoring Soil and Ecosystems
Regenerative agriculture is more than a buzzword—it’s a transformative approach to farming that prioritizes soil health, biodiversity, and carbon sequestration. Unlike conventional agriculture, which often depletes soil nutrients, regenerative practices like cover cropping, crop rotation, and no-till farming work to restore and enrich soil over time.
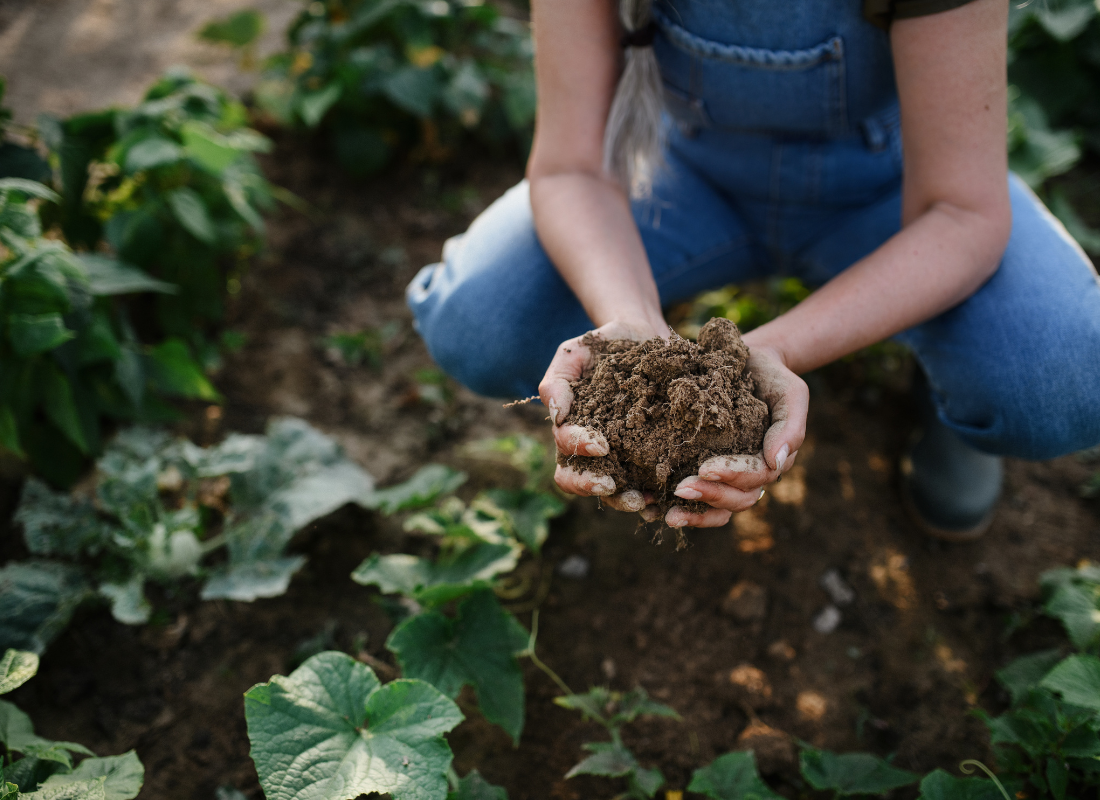 This trend is crucial because healthy soil not only supports biodiversity but also acts as a powerful carbon sink, trapping carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Companies in the food industry can support regenerative agriculture by sourcing from regenerative farms, partnering with local farmers, or offering regenerative-certified products. As consumers become more eco-conscious, regenerative agriculture offers an authentic way for brands to align with sustainability values.
This trend is crucial because healthy soil not only supports biodiversity but also acts as a powerful carbon sink, trapping carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Companies in the food industry can support regenerative agriculture by sourcing from regenerative farms, partnering with local farmers, or offering regenerative-certified products. As consumers become more eco-conscious, regenerative agriculture offers an authentic way for brands to align with sustainability values.
Plant-Based Alternatives: Beyond Meat Substitutes
Plant-based foods continue to dominate the sustainability conversation. With the growing popularity of plant-based meats, dairy alternatives, and even plant-based seafood, the food industry is evolving to meet consumer demand for eco-friendly, ethical choices. Plant-based foods require significantly fewer resources, including land, water, and energy, making them a sustainable option for the planet.
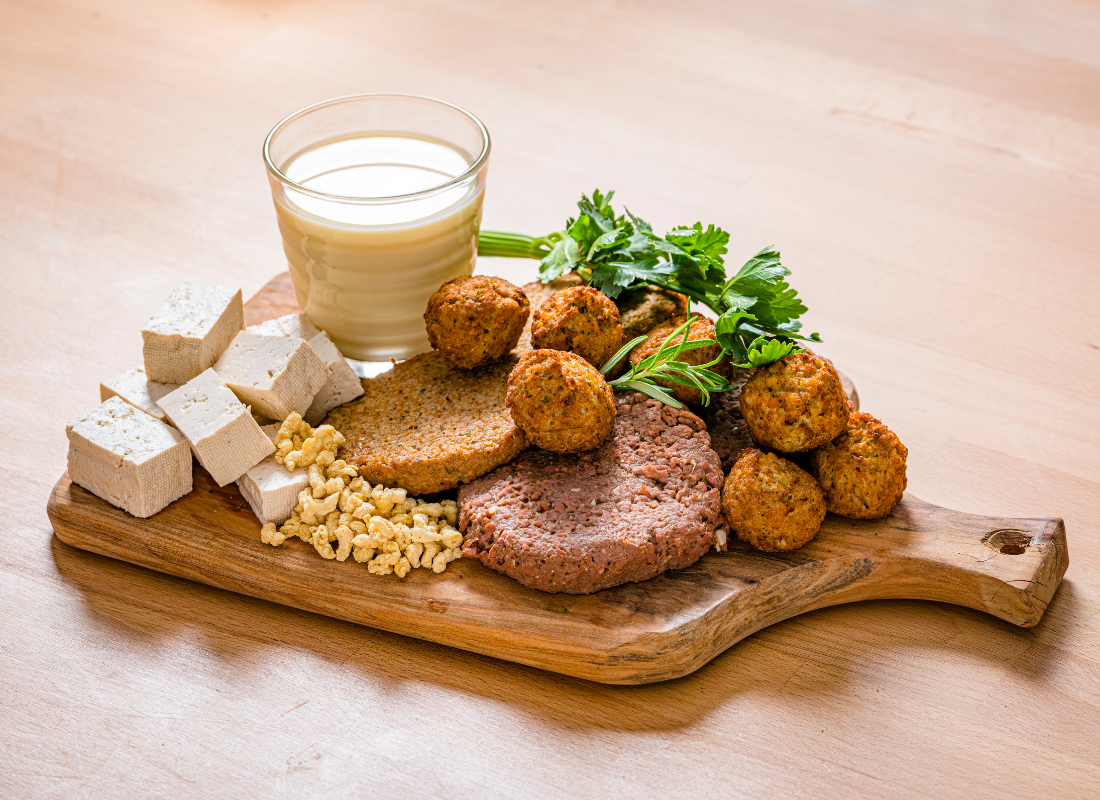

In Switzerland, companies like Planted and The Green Mountain are leading the way with plant-based meat alternatives such as burgers, sausages, and kebabs, all made with simple, sustainable ingredients. New Roots offers vegan cheese options made from organic Swiss almonds, providing a tasty alternative for dairy-free consumers, while Soyana has been pioneering organic plant-based products, including tofu and yogurt alternatives, since 1981. Other players like SwissDeCode support the industry by offering advanced food testing services to ensure the quality and transparency of plant-based products.
This trend extends beyond classic plant-based burgers and milks. In 2025, plant-based innovations are expanding into new categories, from plant-based eggs to seafood alternatives. Companies can embrace this trend by broadening their plant-based offerings, experimenting with new recipes, or creating vegan versions of popular dishes. This not only appeals to vegan and vegetarian consumers but also taps into the growing “flexitarian” market—those who want to reduce their meat intake for health and environmental reasons.
Lab-Grown Meat: Sustainable Protein Production
Lab-grown meat—also known as cultivated or cultured meat—has been generating excitement and debate in the food industry. Produced by cultivating animal cells in controlled lab environments, lab-grown meat replicates the taste and texture of conventional meat without the need for animal farming. This innovation has the potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, land use, and water consumption associated with traditional livestock farming.
Several companies are pioneering this movement, including Aleph Farms from Israel, known for producing the first lab-grown steak, and Upside Foods and Eat Just in California, both of which received regulatory approval to sell lab-grown chicken in the U.S. in 2023. Mosa Meat, a Dutch company, developed the world’s first lab-grown hamburger, while Australia’s Vow is exploring innovative options like exotic cultured meats.
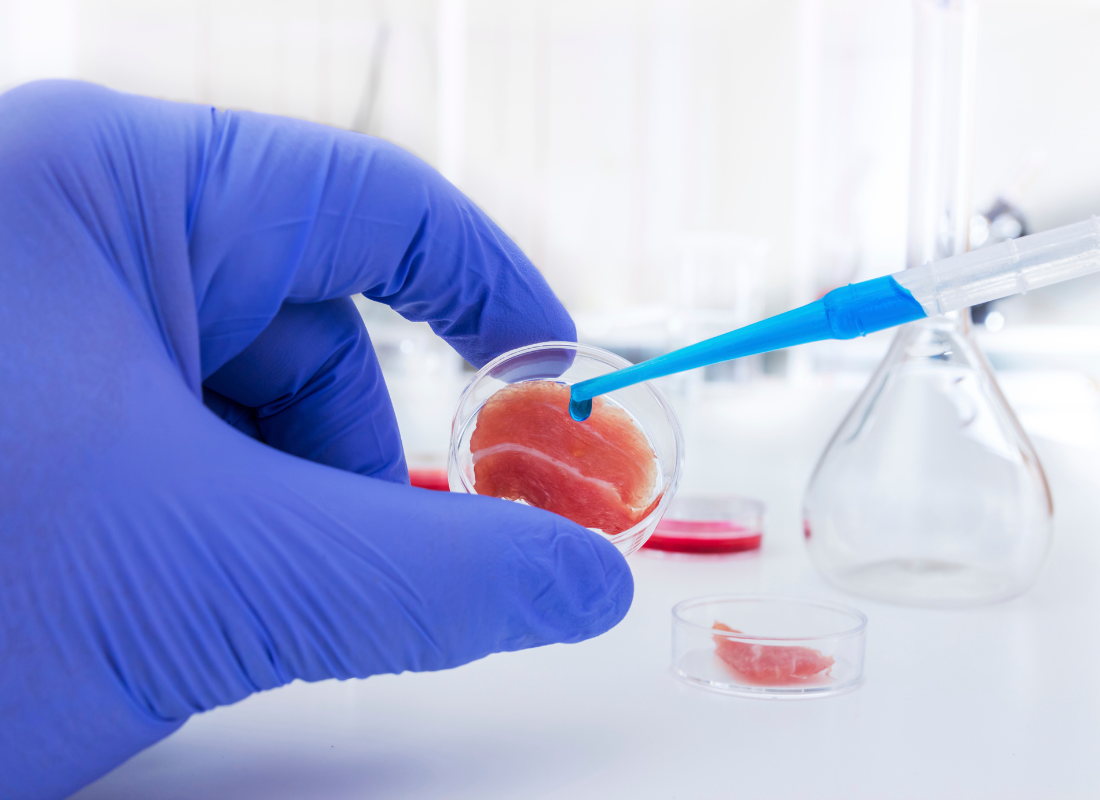 Though lab-grown meat is not yet widely available, regulatory approvals are slowly advancing, and companies are investing heavily in its development. By supporting lab-grown meat, companies can offer a sustainable protein alternative that meets the demands of a growing population while easing pressure on the environment. For food service businesses, partnering with cultured meat brands could provide a unique, eco-friendly option for customers interested in the future of sustainable dining.
Though lab-grown meat is not yet widely available, regulatory approvals are slowly advancing, and companies are investing heavily in its development. By supporting lab-grown meat, companies can offer a sustainable protein alternative that meets the demands of a growing population while easing pressure on the environment. For food service businesses, partnering with cultured meat brands could provide a unique, eco-friendly option for customers interested in the future of sustainable dining.
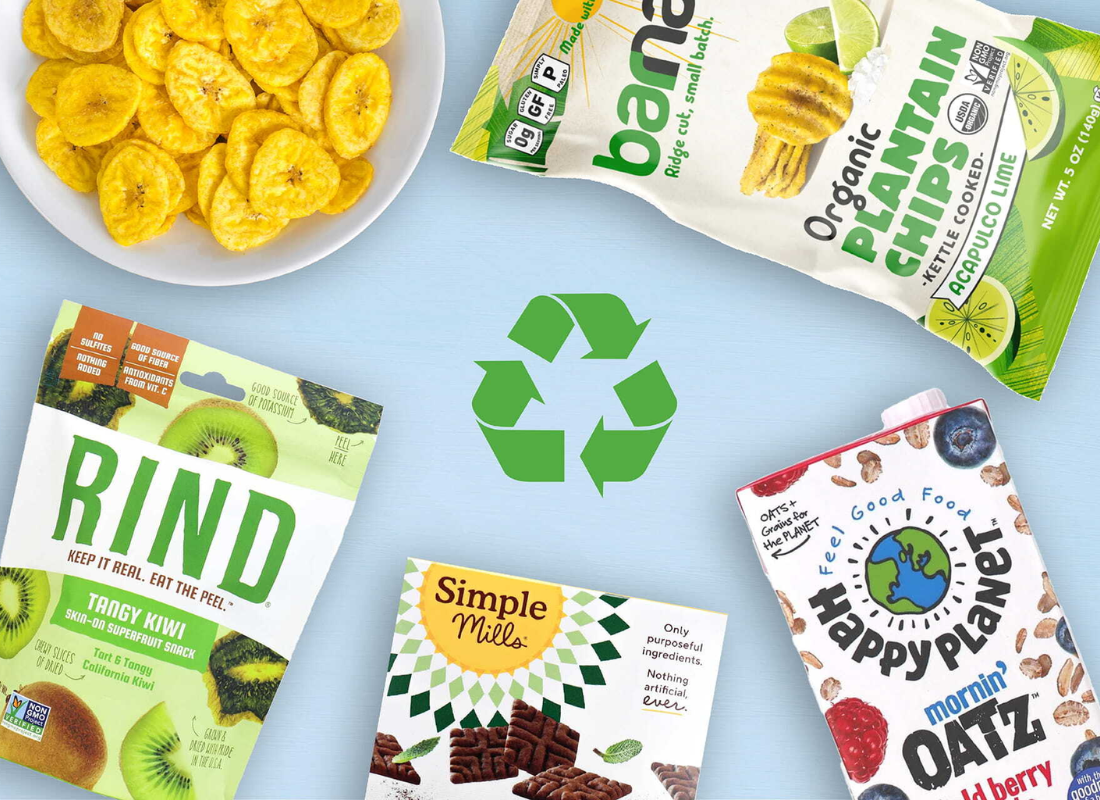
 Upcycled Foods: Reducing Waste by Maximizing Resources
Upcycled Foods: Reducing Waste by Maximizing Resources
Upcycling is one of the most impactful ways to address food waste, which accounts for about 8-10% of global greenhouse gas emissions. Upcycled foods are made from ingredients that would otherwise go to waste, such as juice pulp, spent grains, or “ugly” produce that doesn’t meet aesthetic standards. This trend turns potential waste into valuable food products, helping to reduce emissions and maximize resources.
Brands like ReGrained, which creates snacks from spent grains left over from beer brewing, and Rubies in the Rubble, known for their condiments made from surplus produce, have embraced upcycling. Rind Snacks uses fruit peels and “ugly” fruits to make dried fruit snacks, while Toast Ale brews beer from surplus bread. Swiss-based companies are also joining the movement, such as ResQ Club, which partners with restaurants and cafes to reduce food waste by selling surplus meals to consumers at discounted rates.
 Brands can embrace upcycling by incorporating upcycled ingredients into their products, partnering with companies focused on food waste, or even creating exclusive upcycled product lines. This not only reduces waste but also appeals to consumers who want to support environmentally responsible brands. In 2025, upcycled foods are becoming mainstream, and companies that embrace this trend can position themselves as pioneers in the zero-waste movement.
Brands can embrace upcycling by incorporating upcycled ingredients into their products, partnering with companies focused on food waste, or even creating exclusive upcycled product lines. This not only reduces waste but also appeals to consumers who want to support environmentally responsible brands. In 2025, upcycled foods are becoming mainstream, and companies that embrace this trend can position themselves as pioneers in the zero-waste movement.
Localized Supply Chains: Sourcing Close to Home
Local sourcing is gaining momentum as companies and consumers seek to reduce the “food miles” associated with their meals. By sourcing ingredients from local farms and suppliers, companies can reduce transportation emissions and support local economies, creating a more resilient and sustainable supply chain.
 Localized supply chains not only reduce the carbon footprint but also improve traceability, helping companies meet increasing demands for transparency. Companies can get involved by building relationships with local farmers, focusing on seasonal menus, and communicating the benefits of local sourcing to customers. As climate change disrupts global supply chains, localized sourcing is a proactive way to build sustainability into business operations.
Localized supply chains not only reduce the carbon footprint but also improve traceability, helping companies meet increasing demands for transparency. Companies can get involved by building relationships with local farmers, focusing on seasonal menus, and communicating the benefits of local sourcing to customers. As climate change disrupts global supply chains, localized sourcing is a proactive way to build sustainability into business operations.
Precision Fermentation: A New Frontier in Sustainable Ingredients
Precision fermentation uses microbial fermentation to create essential food ingredients—like dairy proteins, egg whites, and flavor compounds—without traditional animal farming. By fermenting microorganisms in controlled conditions, precision fermentation can produce ingredients with fewer resources, lower emissions, and greater sustainability.
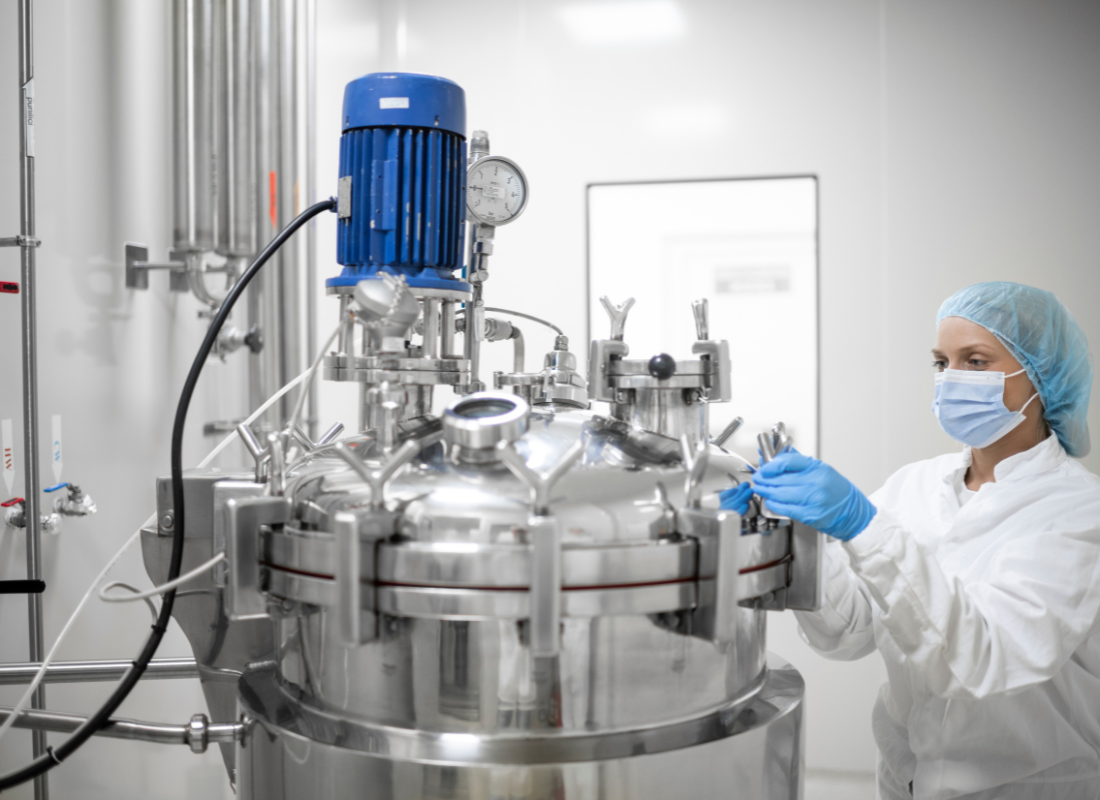 For example, precision fermentation is being used to create vegan dairy proteins that taste and function like traditional dairy, making it a promising solution for people who avoid animal products. Companies can partner with precision fermentation startups, incorporate these ingredients into their product lines, or market them as sustainable options for customers. As the technology advances, precision fermentation will likely become a key player in the shift toward more sustainable food production.
For example, precision fermentation is being used to create vegan dairy proteins that taste and function like traditional dairy, making it a promising solution for people who avoid animal products. Companies can partner with precision fermentation startups, incorporate these ingredients into their product lines, or market them as sustainable options for customers. As the technology advances, precision fermentation will likely become a key player in the shift toward more sustainable food production.
Conclusion: Embracing Sustainable Food Trends in 2025
Sustainability in the food industry is no longer a niche concern. As we face unprecedented environmental challenges, businesses must innovate to meet the needs of eco-conscious consumers. From regenerative agriculture and plant-based foods to lab-grown meat and upcycled products, these sustainable food trends are not only good for the planet—they’re also smart business.
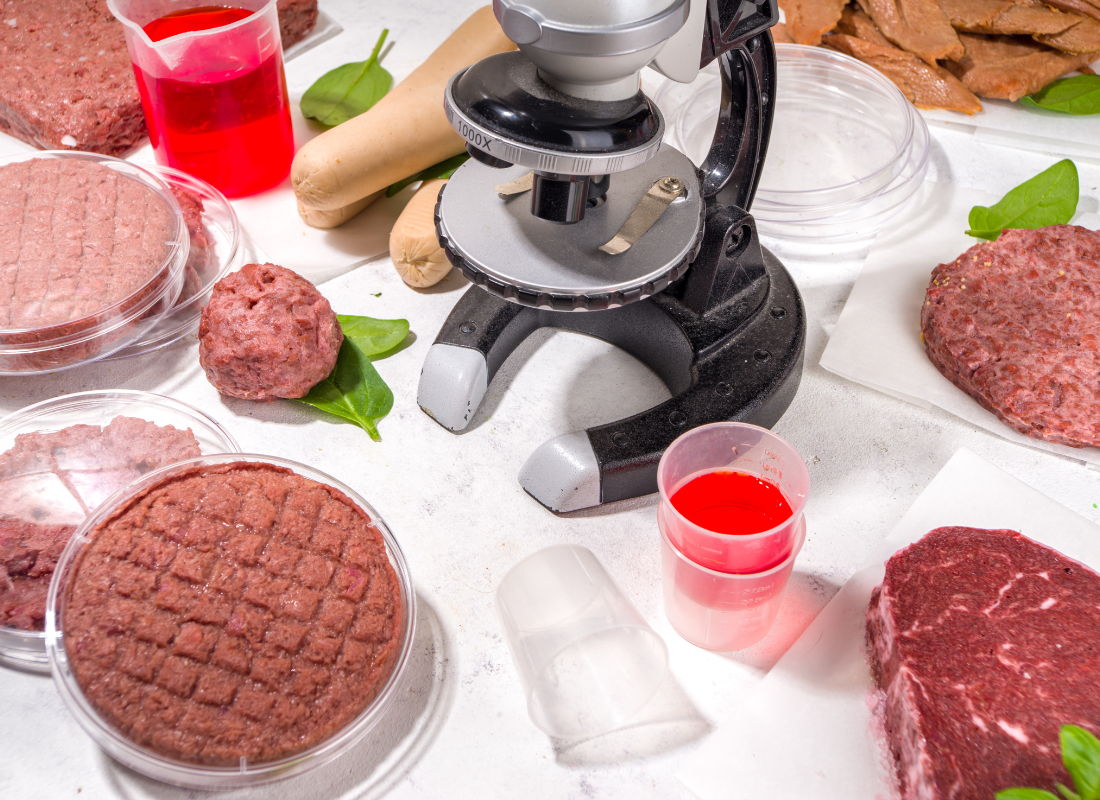 In 2025, companies have a unique opportunity to support sustainable food systems by investing in and promoting these trends. Whether by sourcing from regenerative farms, expanding plant-based menus, or partnering with innovators in lab-grown meat, the choices businesses make today can drive positive change for years to come.
In 2025, companies have a unique opportunity to support sustainable food systems by investing in and promoting these trends. Whether by sourcing from regenerative farms, expanding plant-based menus, or partnering with innovators in lab-grown meat, the choices businesses make today can drive positive change for years to come.
By adopting these practices, companies can lead the way toward a healthier, more sustainable future—one that benefits both people and the planet.




