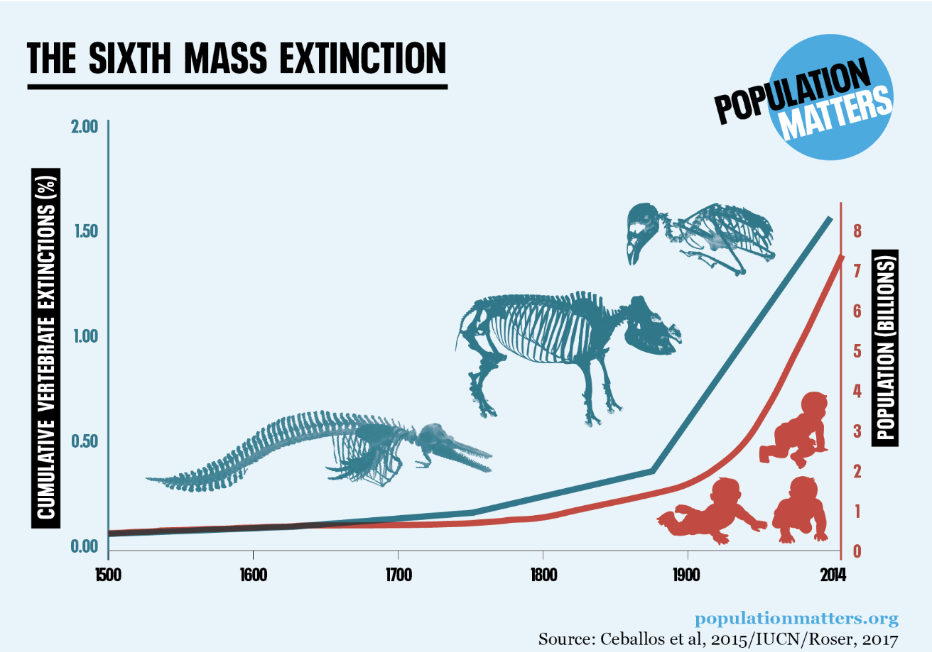
Throughout Earth’s 4.5 billion-year history, five mass extinctions have profoundly shaped the planet’s biodiversity. Today, scientists warn that we are on the brink of a Sixth Mass Extinction—a crisis primarily driven by human activities.
A Rapid Loss of Biodiversity
Research indicates that species are disappearing at an alarming rate, with estimates suggesting that current extinction rates are 100 to 1,000 times higher than the natural background rate. According to the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), over 28,000 species are currently threatened with extinction, ranging from iconic animals like the Sumatran tiger to countless less-known organisms. This crisis is characterized by habitat destruction, pollution, overfishing, and climate change, all exacerbated by human expansion and resource consumption.
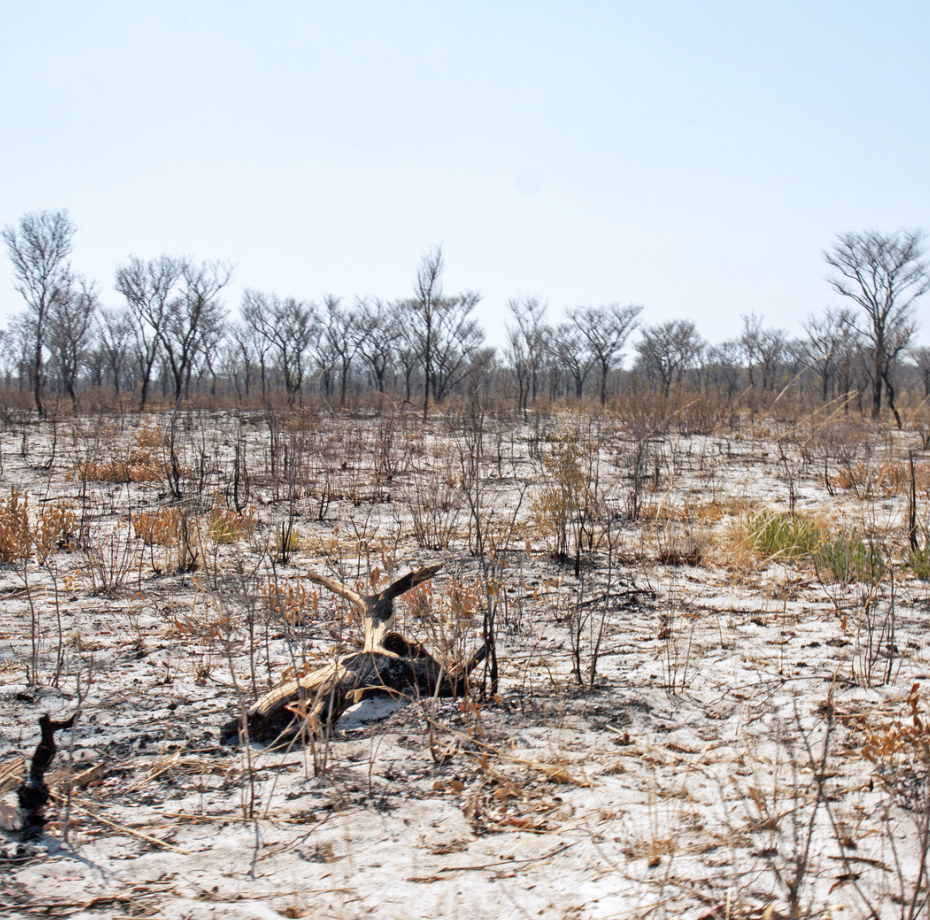

The Human Impact
Human actions have led to significant habitat loss, especially in biodiversity hotspots such as rainforests and coral reefs. The World Wildlife Fund (WWF) states that around 50% of the world’s forests have been cleared, leading to a cascade of ecological consequences. Habitat destruction, along with climate change, results in altered species distributions and increased vulnerability. Overfishing threatens marine ecosystems, while pollution introduces harmful chemicals into food chains, adversely affecting both wildlife and human health.
Why Should We Care?
Biodiversity is critical not only for the health of ecosystems but also for human survival. The loss of species disrupts essential ecological services, such as pollination, water purification, and carbon sequestration. The extinction of key species can destabilize food chains and threaten the livelihoods of communities dependent on natural resources. For example, the decline of pollinators like bees can directly impact food production, leading to increased prices and food scarcity.
Pathways to Solutions
While the situation is dire, there are pathways to mitigate the crisis:
- Advocate for Sustainable Practices: Encourage local businesses and governments to adopt sustainable practices. This includes reducing waste, conserving water, and promoting renewable energy sources. Individuals can advocate for policies that protect habitats and endangered species.
- Reduce Your Ecological Footprint: Make informed choices about consumption. Opt for sustainable products, reduce meat consumption, minimize plastic use, and support local and organic farms. Every small action contributes to a larger impact.
- Engage in Reforestation and Restoration Projects**: Participate in or support reforestation initiatives in your community. Trees are vital for carbon sequestration, and restoring degraded land helps to reestablish ecosystems.
- Educate and Raise Awareness: Share knowledge about biodiversity and the importance of conservation within your community. Organize workshops, participate in social media campaigns, or host events focused on environmental awareness.
- Support Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)**: The United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals include targets for biodiversity conservation. Engaging with these goals at the local level can amplify efforts to protect our planet.
The Sixth Mass Extinction poses an unprecedented threat to our planet. However, with awareness, action, and global cooperation, we have the power to change our trajectory. By recognizing the intrinsic value of biodiversity, we can work toward a sustainable future where both humans and wildlife can thrive.
As we reflect on our role in this critical moment, let us remember: protecting biodiversity is not just an environmental issue; it’s a matter of survival. Together, we can advocate for a world where nature is valued and preserved, ensuring a legacy of life for generations to come.
For further reading, check out these sources:
– [WWF Report on Biodiversity Loss] (https://www.worldwildlife.org/pages/why-biodiversity-matters)
– [IUCN Red List] (https://www.iucnredlist.org/)
– [United Nations Biodiversity Framework] (https://www.cbd.int/article/30by30)





