
The term “Plastic” is derived from the Greek word “Plastikos”, meaning “Malleable”. This refers to the plasticity or malleability of the material during manufacture, which allows it to take on a variety of forms such as films, fibers, sheets, tubes, bottles and boxes.
Plastic is made through a chemical process called polymerization, which involves the combination of small molecules called monomers to form long chains called polymers.
Here’s a simplified explanation of how plastic is made:
-
Raw Materials
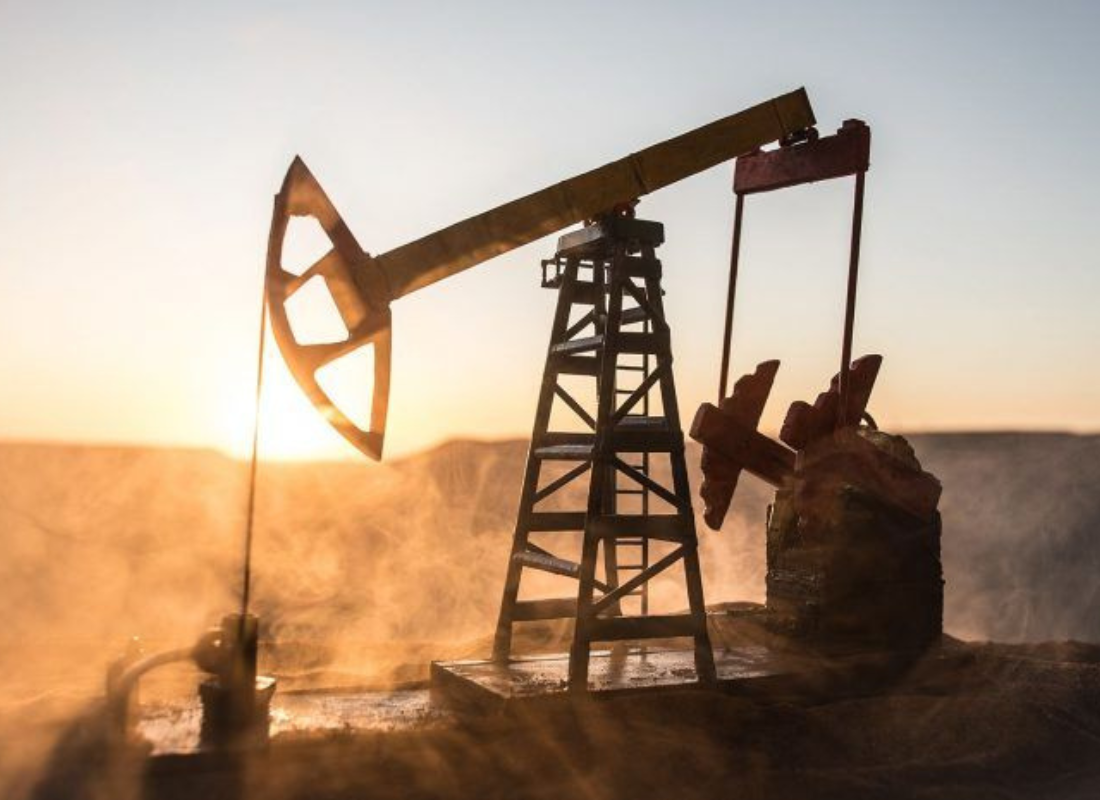 The primary raw materials used in plastic production are derived from fossil fuels, particularly crude oil and natural gas. These raw materials are refined to obtain basic building blocks such as ethylene, propylene, and styrene, which serve as monomers for various types of plastics.
The primary raw materials used in plastic production are derived from fossil fuels, particularly crude oil and natural gas. These raw materials are refined to obtain basic building blocks such as ethylene, propylene, and styrene, which serve as monomers for various types of plastics.
-
Polymerization
 The monomer molecules undergo polymerization, a chemical reaction in which they join together to form long chains or networks. This process is typically facilitated by catalysts, heat, or pressure, depending on the type of plastic being produced.
The monomer molecules undergo polymerization, a chemical reaction in which they join together to form long chains or networks. This process is typically facilitated by catalysts, heat, or pressure, depending on the type of plastic being produced.
-
Additives
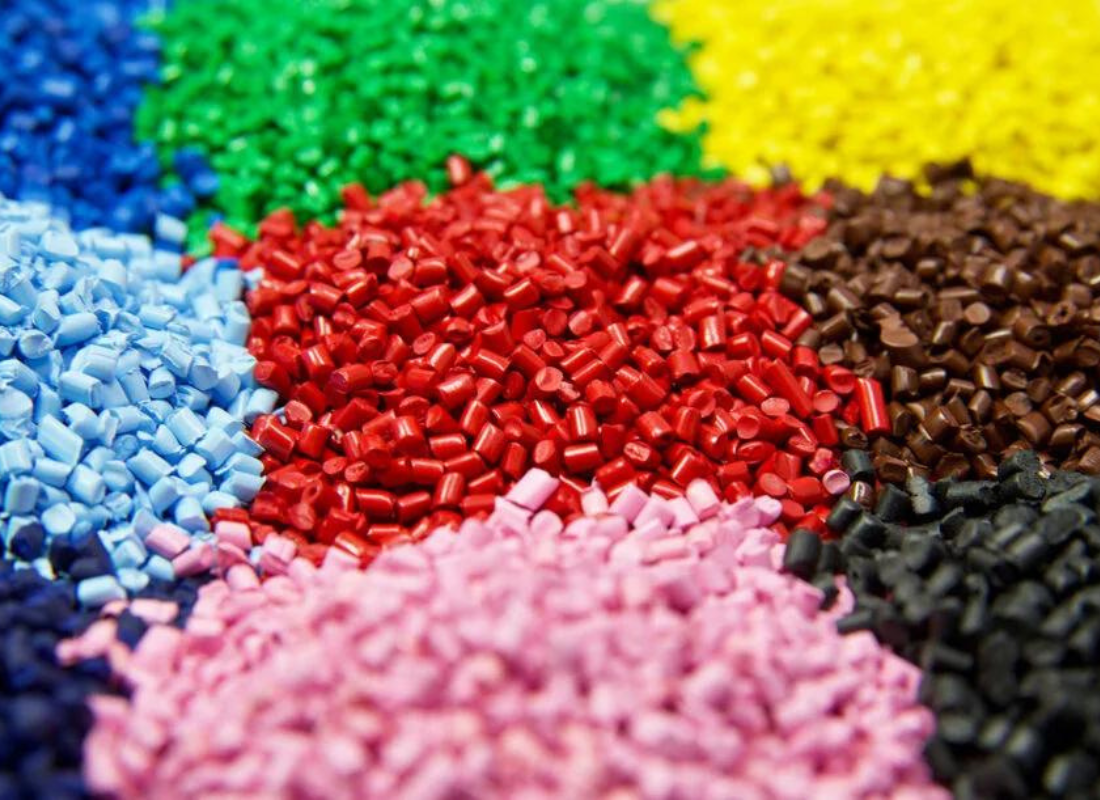 During polymerization, various additives may be incorporated into the plastic to impart specific properties such as color, flexibility, strength, or resistance to heat and chemicals. Additives can include plasticizers, stabilizers, fillers, pigments, and flame retardants.
During polymerization, various additives may be incorporated into the plastic to impart specific properties such as color, flexibility, strength, or resistance to heat and chemicals. Additives can include plasticizers, stabilizers, fillers, pigments, and flame retardants.
-
Processing
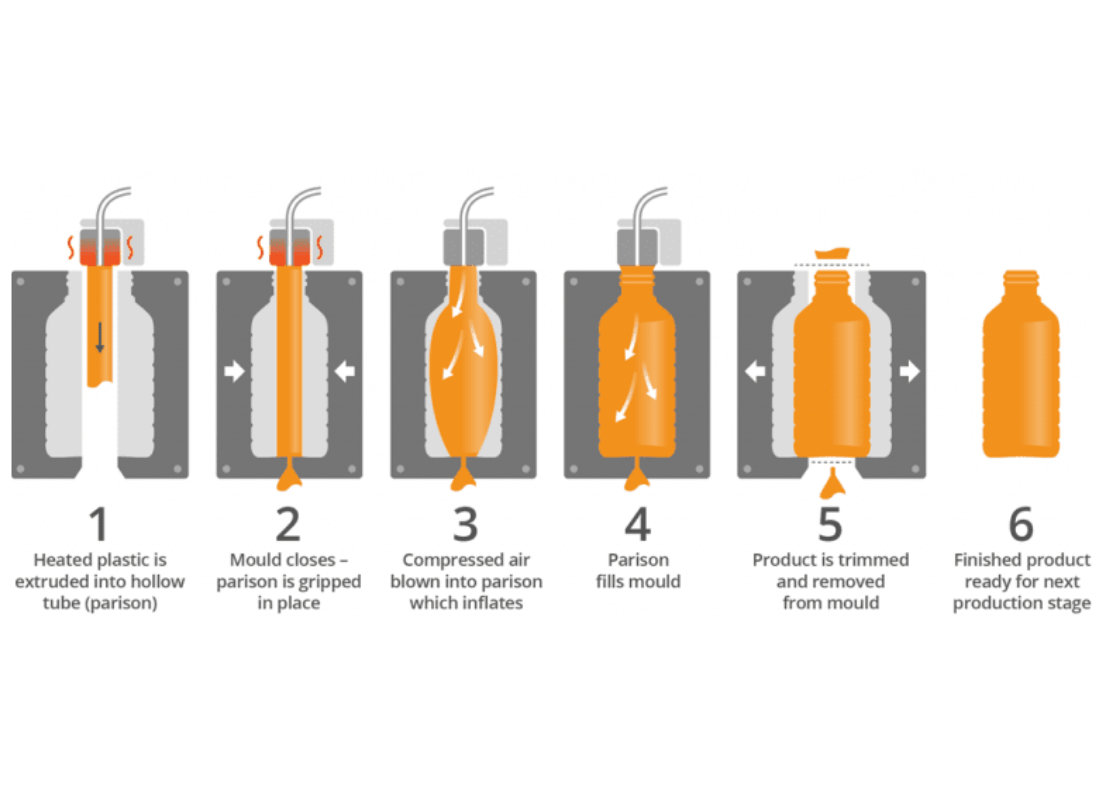 Once polymerization is complete, the resulting polymer is processed into the desired shape and form. This can involve techniques such as extrusion, injection molding, blow molding, or thermoforming, depending on the intended application of the plastic.
Once polymerization is complete, the resulting polymer is processed into the desired shape and form. This can involve techniques such as extrusion, injection molding, blow molding, or thermoforming, depending on the intended application of the plastic.
-
Final Product
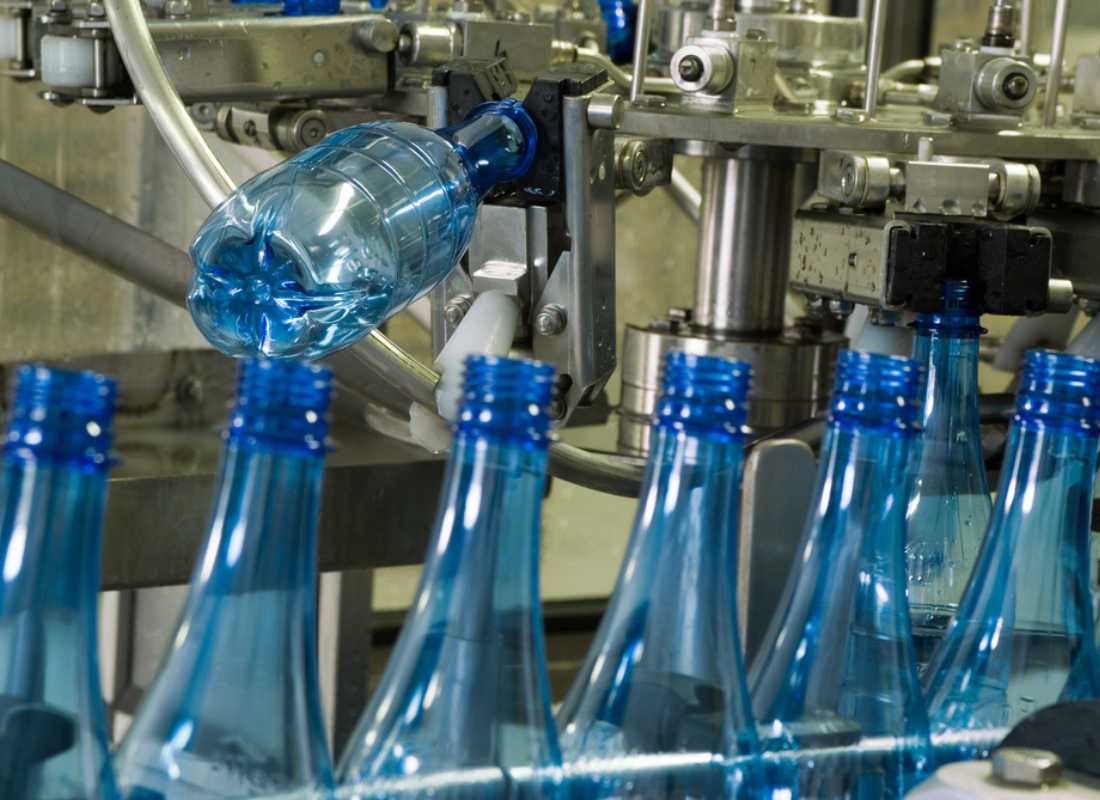 The processed plastic is then cooled, solidified, and prepared for distribution and use. It may be further treated or finished to meet specific quality standards or customer requirements.
The processed plastic is then cooled, solidified, and prepared for distribution and use. It may be further treated or finished to meet specific quality standards or customer requirements.
-
End-of-Life
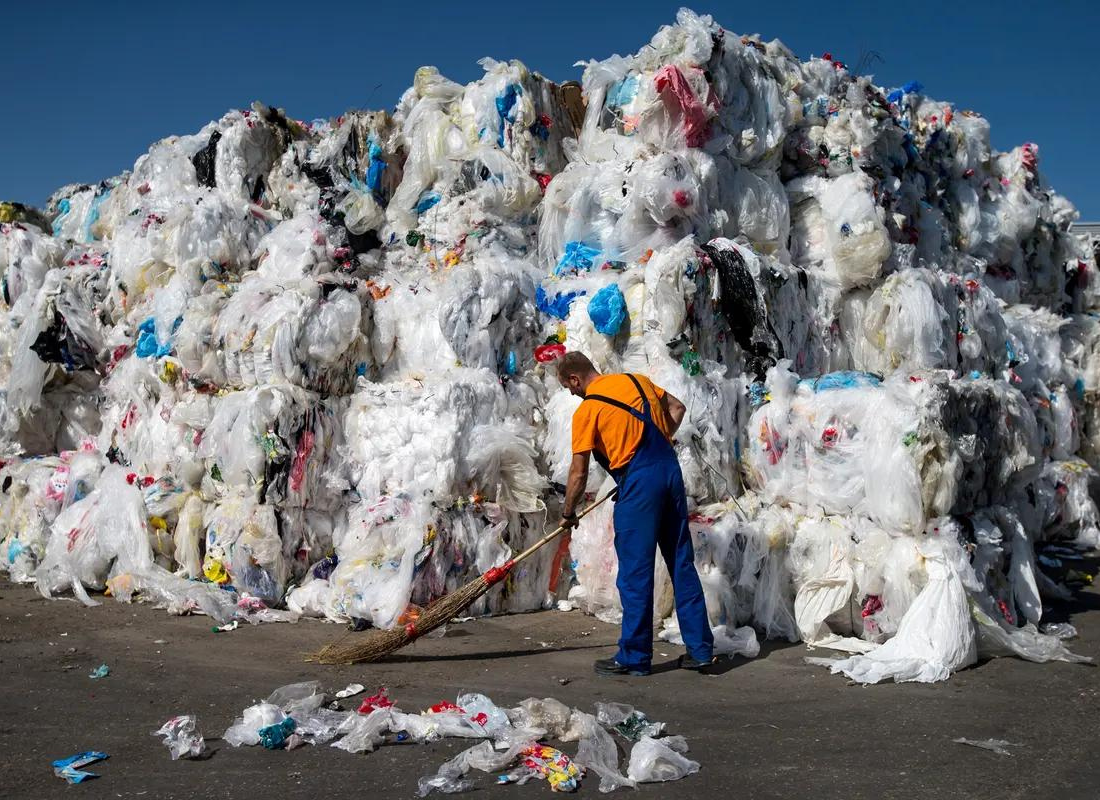 After use, plastic products may be recycled, incinerated, or disposed of in landfills. Recycling involves breaking down the plastic into its constituent monomers or converting it into new products, while incineration and landfill disposal can contribute to environmental pollution and waste management challenges.
After use, plastic products may be recycled, incinerated, or disposed of in landfills. Recycling involves breaking down the plastic into its constituent monomers or converting it into new products, while incineration and landfill disposal can contribute to environmental pollution and waste management challenges.
-
Environmental Considerations
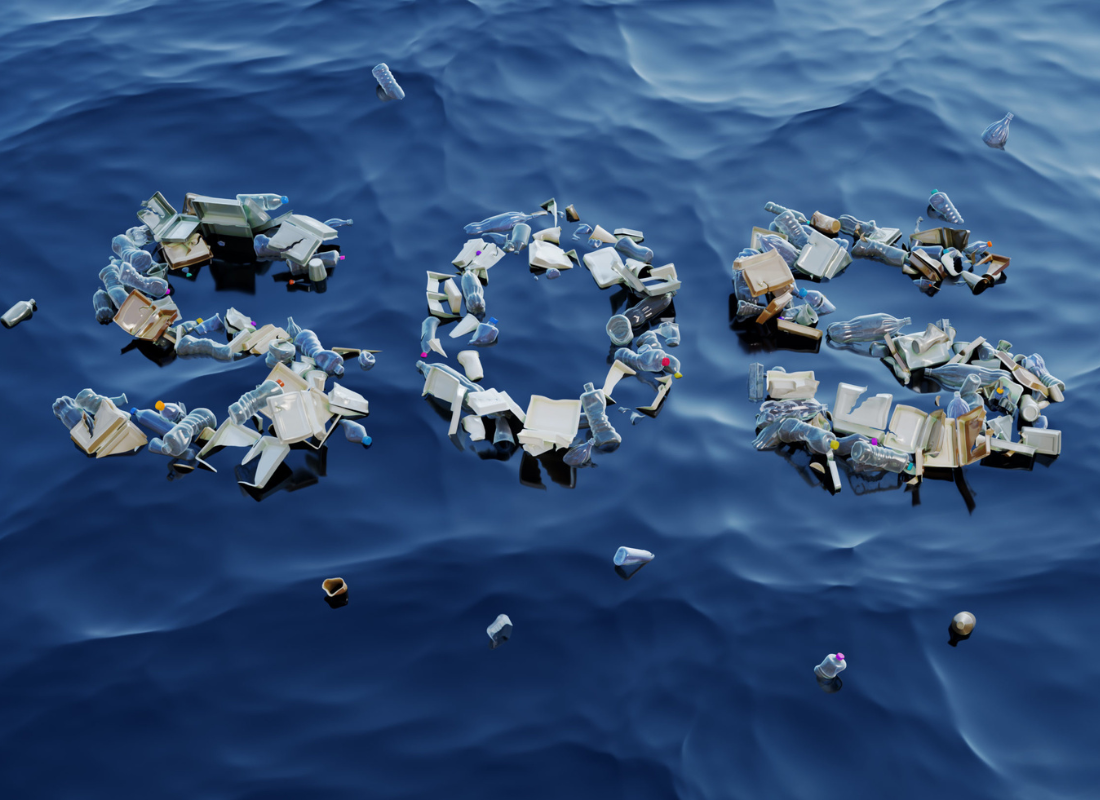

Plastic production can have significant environmental impacts, including resource depletion, energy consumption, greenhouse gas emissions, and pollution. Efforts are underway to develop more sustainable and environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional plastics, such as bio-based plastics, biodegradable plastics, and recycled plastics.
CONCLUSION
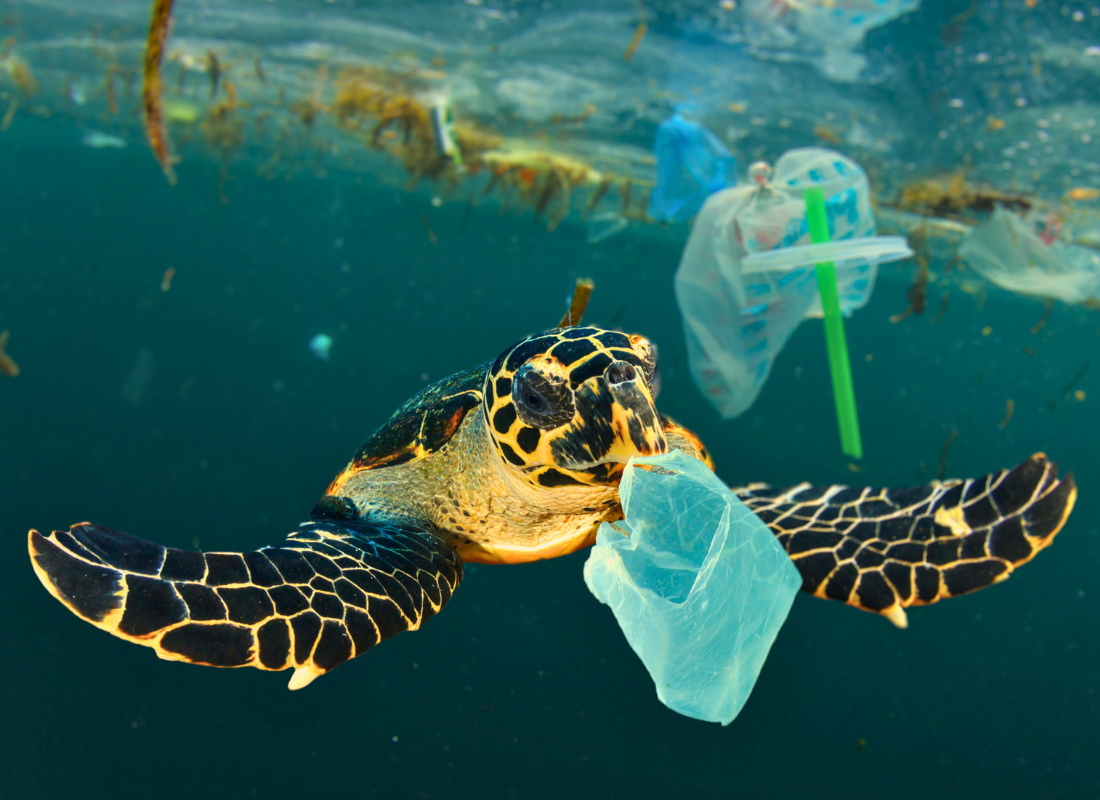

It’s important to note that plastic production can vary significantly depending on the type of plastic being manufactured, as well as the specific manufacturing processes and technologies used by different industries and manufacturers. Additionally, efforts are underway to develop more sustainable alternatives to traditional plastics, such as biodegradable plastics and materials derived from renewable sources, to mitigate the environmental impact of plastic production and disposal.
Sources:
https://plasticseurope.org/plastics-explained/how-plastics-are-made/
https://pagev.org/how-plastic-is-made
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Plastic




